Each dot or slot blot would contain known amounts of target protein or cell lysate. Once dry, dot blots and slot blots are subjected to the same immunodetection steps used for Western blotting, i.e. Blocking, antibody incubation, and target detection with substrate. The Basic Protocol describes such a procedure for dot or slot blotting on an uncharged nylon membrane; annotations to the steps detail the minor modifications that are needed if blotting onto nitrocellulose. The first alternate protocol describes the more major changes required for blotting with a positively charged nylon membrane. Introduction The blotting protocol described below is suitable for majority of protein blotting applications using the XCell II ™ Blot Module. However, some optimization may be necessary by the user to obtain the best results (page 21). Materials Needed Previously electrophoresed mini-gels (maximum gel size 9 cm × 9 cm).
Blotting is primarily used in molecular biology. It is used to identify proteins and nucleic acids for diagnostic purpose. Specifically, blotting is used for identifying biomolecules like DNA, mRNA, and protein during gene expression.
DNA and RNA molecules need to undergo biochemistry analysis and they are separated using the blotting method.
Picture : A helpful mnemonic for students to remember the relation between various blotting methods and its uses
Blotting is done by enabling the mixture of molecule pass through a gel that separates the molecules based on their molecular size. The molecules being tested are hard-pressed against a membrane which will then transfer the molecule from the gel onto the suitable membrane through capillary action.
One of the commonly used blotting procedures is Southern blotting. This procedure was introduced in 1975 by Edwin Southern; thus, where the name was taken. What is Southern blotting? It is a blotting method used to detect a particular sequence of DNA in a DNA sample. There are other subtypes such as Northern blotting, Western blotting, South-Western blotting, and Eastern blotting. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Image 1: The Southern blot procedure as shown in the image above.
Picture Source: thescienceinfo.com
What does Southern blotting reveal?
A southern blot analysis reveals the following:
- Identity of the DNA
- Size of the DNA
- Abundance of the DNA (4, 5)
The Southern blotting method is a classic technique that separates DNA fragments according to their size through electrophoresis. They will be transferred to a membrane, hybridize, washed, and lastly, detecting the labeled DNA band.
How much DNA is needed for Southern blotting?
The amount of DNA needed varies depending on the size and specific activity of the probe.
What is the principle of Southern blotting?
Southern blotting is a restriction fragment length polymorphism. It is a hybridization method for identifying the size of DNA from a mixture of other similar molecules. Basically, Southern blotting separates DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are identified using a labeled probe hybridization. (5, 6, and 7)
What are the steps in Southern blotting?
There are a series of steps that need to be strictly followed when performing Southern blotting. They are the following:
Image 2: The first and second step of southern blot method.
Picture Source: slideplayer.com
#1 – Restriction Digest
A restriction enzyme is used to fragmentize the DNA. The DNA is cut at a specific site generating a fragment. The DNA fragments obtained by restriction digest are amplified by PCR. (7, 8)
#2 – Gel electrophoresis
Once the DNA fragments are obtained, the next step is separating the DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis.
Casino waitress uniform. Image 3: The denaturing of DNA.
Picture Source: slidesharecdn.com
#3 – Denaturation
An SDS gel is needed in this step. Once electrophoresis is done, the SDS gel is soaked in either acid like HCl or alkali like NaOH. The purpose is to denature the fragments of double-stranded DNA. After denaturation, the strands of DNA will separate. (8, 9)
Casino nl vertaling en. #4 – Blotting
This is where the actual bloating takes place. The DNA's separated strands are transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane through the process of blotting.
Blotting process is done so as to determine the nature of DNA
#5 – Baking and Blocking
The DNA is based on autoclave and fix in the membrane. Casein or Bovine serum albumin is used to treat the membrane. What these chemicals do is they saturate the membrane's binding site.
#6 – Hybridization with labeled probes Dogs gambling painting meaning.
A labeled probe is used to treat the membrane-bound DNA. It has complementary sequences to the gene being studied on. The probe will bind with the complementary DNA on the membrane. (3, 7, and 10)
#7 – Visualization by Autoradiogram
An autoradiogram is used to visualize the membrane bound DNA that is labeled with a probe. Autoradiogram visualization provides a pattern of bands.
Why is Southern blotting important?
Image 5: A southern blot is one of the procedures used in paternity testing.
Picture Source: slideplayer.com
Southern blotting is important as it is useful in the various field of interest such as:
- It is used in detecting the DNA in a given sample such as DNA fingerprinting in forensics.
- It is useful in isolating and identifying the gene of interest.
- In forensics, southern blotting is one of the commonly used procedures, especially in:
- Criminal identification
- Victim identification
- It is used for paternity testing.
- It helps identify gene rearrangement or mutation in a particular sequence of DNA/gene mapping.
- It is used to diagnose a particular disease caused by genetic defects.
- It is helpful in identifying infectious agents.
- It helps in restricting fragment length polymorphism.
- It has the ability to identify a single gene in a pool of DNA fragments.
- It helps detect cancer and genetic diseases like sickle cell mutation and monoclonal leukemia. (1, 3, 5, and 8)
How is Southern blotting used in forensics?
Forensic laboratories used southern blotting method to detect the smallest quantity of DNA, especially in the case of rape, thieves, or identification of parenthood. (7, 8)
Image 6: Southern blotting is a procedure used in a forensic setting such as in the case of rape and other types of crimes that may require identification of DNA samples.
Picture Source: newyorker.com
Summary
Southern blot is a method commonly used in molecular biology. It has been a widely used technique for over three decades. Through southern blot, researchers can thoroughly understand the fundamentals of molecular biology. The primary purpose of southern blot is to detect a sequence of DNA in a given DNA sample.
However, the southern blotting method can be quite expensive and extremely technical in nature. Sample-wise, it needs a large quantity of DNA, which is not always favorable in some settings.
With the advancement in the field of science and medicine, new DNA testing methods were developed such as PCR. It is better than southern blotting because the procedure involved is very straightforward. It is easy, fast, reliable, and only requires a small volume of DNA. (2, 4, 6, and 9)
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Southern_blot
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/southern-blotting-principle-procedure-application/
- https://www.thermofisher.com/ph/en/home/life-science/dna-rna-purification-analysis/nucleic-acid-gel-electrophoresis/southern-blotting.html
- https://askabiologist.asu.edu/southern-blotting
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/southern-blot
- https://www.mybiosource.com/learn/southern-blotting/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18432697
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-Southern-Blotting.aspx
- https://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Gr12-18.html
- https://www.nature.com/wls/definition/southern-blot-289
Related Posts:
The best results for Western blots are obtained when both the primary and secondary antibodies are accurately titrated. Although dot blots cannot determine the molecular weight or integrity of a protein and therefore should never be used to identify a protein per se, they are particularly useful in titrating antibodies. Optimal antibody concentrations can be efficiently determined by adhering proteins to nitrocellulose using a dot blot technique with a checkerboard pattern to determine the optimal primary: secondary concentration pair.
Below are guidelines and general protocols for performing dot blots either by using a microfiltration unit or by manually spotting protein onto a membrane.

Dot blot Overview
Dot blots are similar to Western blots, however the proteins are not separated electrophoretically prior to transfer to a membrane but are instead spotted directly onto a membrane. Because proteins are not first separated using a gel, dot blots cannot be used to determine the molecular weight of a protein nor can they discriminate between alternate forms of the protein (e.g. cleaved proteins). However when the integrity and identity of the protein is known, the dot blot format can be used to provide substrates for titration of antibodies.

A labeled probe is used to treat the membrane-bound DNA. It has complementary sequences to the gene being studied on. The probe will bind with the complementary DNA on the membrane. (3, 7, and 10)
#7 – Visualization by Autoradiogram
An autoradiogram is used to visualize the membrane bound DNA that is labeled with a probe. Autoradiogram visualization provides a pattern of bands.
Why is Southern blotting important?
Image 5: A southern blot is one of the procedures used in paternity testing.
Picture Source: slideplayer.com
Southern blotting is important as it is useful in the various field of interest such as:
- It is used in detecting the DNA in a given sample such as DNA fingerprinting in forensics.
- It is useful in isolating and identifying the gene of interest.
- In forensics, southern blotting is one of the commonly used procedures, especially in:
- Criminal identification
- Victim identification
- It is used for paternity testing.
- It helps identify gene rearrangement or mutation in a particular sequence of DNA/gene mapping.
- It is used to diagnose a particular disease caused by genetic defects.
- It is helpful in identifying infectious agents.
- It helps in restricting fragment length polymorphism.
- It has the ability to identify a single gene in a pool of DNA fragments.
- It helps detect cancer and genetic diseases like sickle cell mutation and monoclonal leukemia. (1, 3, 5, and 8)
How is Southern blotting used in forensics?
Forensic laboratories used southern blotting method to detect the smallest quantity of DNA, especially in the case of rape, thieves, or identification of parenthood. (7, 8)
Image 6: Southern blotting is a procedure used in a forensic setting such as in the case of rape and other types of crimes that may require identification of DNA samples.
Picture Source: newyorker.com
Summary
Southern blot is a method commonly used in molecular biology. It has been a widely used technique for over three decades. Through southern blot, researchers can thoroughly understand the fundamentals of molecular biology. The primary purpose of southern blot is to detect a sequence of DNA in a given DNA sample.
However, the southern blotting method can be quite expensive and extremely technical in nature. Sample-wise, it needs a large quantity of DNA, which is not always favorable in some settings.
With the advancement in the field of science and medicine, new DNA testing methods were developed such as PCR. It is better than southern blotting because the procedure involved is very straightforward. It is easy, fast, reliable, and only requires a small volume of DNA. (2, 4, 6, and 9)
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Southern_blot
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/southern-blotting-principle-procedure-application/
- https://www.thermofisher.com/ph/en/home/life-science/dna-rna-purification-analysis/nucleic-acid-gel-electrophoresis/southern-blotting.html
- https://askabiologist.asu.edu/southern-blotting
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/southern-blot
- https://www.mybiosource.com/learn/southern-blotting/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18432697
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-Southern-Blotting.aspx
- https://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Gr12-18.html
- https://www.nature.com/wls/definition/southern-blot-289
Related Posts:
The best results for Western blots are obtained when both the primary and secondary antibodies are accurately titrated. Although dot blots cannot determine the molecular weight or integrity of a protein and therefore should never be used to identify a protein per se, they are particularly useful in titrating antibodies. Optimal antibody concentrations can be efficiently determined by adhering proteins to nitrocellulose using a dot blot technique with a checkerboard pattern to determine the optimal primary: secondary concentration pair.
Below are guidelines and general protocols for performing dot blots either by using a microfiltration unit or by manually spotting protein onto a membrane.
Dot blot Overview
Dot blots are similar to Western blots, however the proteins are not separated electrophoretically prior to transfer to a membrane but are instead spotted directly onto a membrane. Because proteins are not first separated using a gel, dot blots cannot be used to determine the molecular weight of a protein nor can they discriminate between alternate forms of the protein (e.g. cleaved proteins). However when the integrity and identity of the protein is known, the dot blot format can be used to provide substrates for titration of antibodies.
Commercially available units for dot blotting
Dot blots can be performed using commercially available apparatuses, often called microfiltration units. Microfiltration units provide an ease of use as protein blotting, incubations and washes can all be performed within the unit which isolates each individual blot.
Manual dot blots
Dot blots can also be performed without the aid of a microfiltration unit. In this case, protein is spotted manually onto the membrane in a series of small dots. The region containing each dot must then be individually excised and treated separately for incubations and washes.
Samples for dot blots
Protein samples for titrating antibodies should contain the protein of interest in abundance. Recombinant protein is ideal, however cell lysates containing highly expressed protein can also be used.
Negative control samples can also be included, particularly if cell lysates are used. Negative control samples will determine whether any observed signal is due to non-specific cross-reactivity.
Preparation of samples
Although sample preparation for dot blotting is similar to sample preparation for traditional Western blotting, several factors should be kept in mind. These apply both to when using microfiltration units or when spotting the protein manually.
- Prepare enough sample in sufficient volume to accommodate all the conditions being tested
- Do not prepare samples in buffers containing detergents as they will inhibit binding of the protein to the membrane
- If detergents are present, dilute the samples with buffer
- If a sample contains precipitates, centrifuge the sample and only apply the supernatant to membrane to prevent clogging
- Dilute viscous samples in buffer
Dot blot diagram/conditions
Southern Blot : Principle, Protocol (steps) And Uses ..
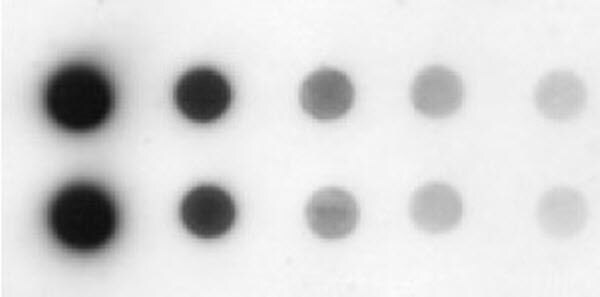
Titration of both primary and secondary antibodies can be performed simultaneously by using a checkerboard titration pattern. Figure 1 is an example of an experiment to titrate a primary antibody with a recommended dilution of 1:1000 and a secondary antibody with a recommended dilution of 1:10,000.
The following guidelines should be followed when planning the experiment:
- Create a diagram of experimental conditions (similar to Figure 1)
- Plan to titrate primary and secondary antibodies on opposing axes
- Choose ranges of antibody dilutions that encompass the recommended concentration and two dilutions above and below the recommended concentration. For example, for an antibody with a recommended dilution of 1:1000, use dilutions of 1:250, 1:500, 1:1000, 1:2000 and 1:4000
- Include spaces containing no primary or secondary antibodies to control for background
Dot blot procedure using a commercial apparatus
Commercial dot blot apparatuses immobilize, concentrate and bind samples to membranes using a vacuum to draw the sample onto the membrane. Washes and antibody incubations can also be performed using the units. Dot blot apparatuses can utilize either a slot blot template that binds the protein to the membrane in a thin slit or a round template for application of the protein in a circle. The slot format is preferred for densitometry and quantitation, however the round format is technically easier to work with because it decreases bubble formation.
Protein Slot Blot Protocol Assay
Follow the manufacturer's instructions to set up and prepare the apparatus.
General protocol
- Apply the sample in a volume large enough to cover the exposed membrane in each well
- Apply sample in the center of the well being careful to avoid creating air bubbles
- Do not exceed binding capacity of the membrane
- Close off unused wells by filling them with sample buffer
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions to draw the sample through the membrane using the vacuum
- Perform washes and incubations according to the manufacturer's guidelines
- Remove membrane from the unit and perform ECL detection using a standard kit
Dot blot procedure using a manual spotting method
Protocol: Dot Blot Checkerboard Titration Of Antibodies ..
A manual dot blot procedure follows the same principal as when using a dot blot apparatus, however the areas in which the proteins are spotted must be delineated by drawing a grid on the membrane. Due to sample diffusion, smaller volumes must be used when manually spotting proteins. After blotting, samples must be physically separated by cutting the membrane prior to incubation with antibodies.
- Delineate spotting areas by drawing a grid on the membrane using a pencil. Maintain a 1cm minimum distance between samples
- Build a stack to accommodate the membrane
- Place paper towels on work surface; enough towels should be used to keep bottom towels dry throughout procedure
- Place dry filter paper on top of paper towels
- Place filter paper prewet with buffer on dry filter paper
- Place prewet membrane on filter paper
- Spot samples onto membrane
- Spot 1-5 microliters of each sample onto center of each marked square in the grid marked on the membrane
- Choose a sample volume that will not spread between squares on the grid and will not exceed the binding capacity of the membrane
- For greater than 2 microliters, apply 2 microliters, allow sample to absorb, then add additional sample to same spot
- Do not exceed binding capacity of membrane
- Sample should wick into membrane and not spread across membrane. Membranes that are too wet will cause spreading of sample
- Place membrane on clean filter paper to dry after sample is absorbed
- Following the grid lines, cut a square around each circle and place each membrane into a separate container
- Fishing tackle boxes work well for titrating antibodies
- Wash and incubate each square with the specified primary and secondary antibody combinations following a standard Western blot protocol
- Perform ECL detection using a standard kit
Protein Slot Blot Protocol Definition
Photo courtesy of Stinging Eyes.